Bandwidth Monitoring Tools
Use NetFlow, jFlow, and sFlow to monitor network bandwidth and application traffic.
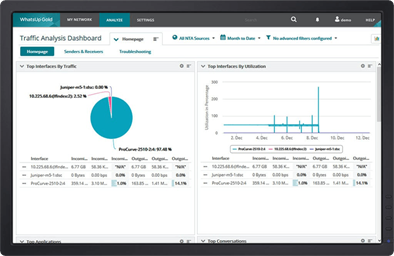
WhatsUp Gold’s bandwidth monitoring tools collect, monitor and analyze network traffic volume by end-point (user), port, interface and protocol (application).
Assure adequate bandwidth for business-critical applications
Minimize the impact of non-critical or unauthorized network traffic
Identify bandwidth hogging processes unnecessarily running in peak load periods
Alert potential DDoS attacks or externally initiated port-scans
Capabilities of WhatsUp Gold Bandwidth Monitoring
WhatsUp Gold tracks bandwidth usage over all areas of the network – devices, applications, servers, link connections, leased lines etc, and offers insights into network bandwidth utilization and traffics analysis. It also maps out historical trends for capacity planning and proactively identifies security issues.
Real-time Bandwidth Monitoring
Real-time monitoring allows administrators to identify interfaces/links/applications/users/protocols taking up bandwidth. WhatsUp Gold can highlight bandwidth utilization over LAN, WAN links and specific devices, identifies internal and external traffic sources/destinations. It also classifies the information as Top speakers, Top Protocols, Top Applications that use up bandwidth.
Apply QoS policies
By default, each network channel operates on a best-effort basis – every application gets equal priority, be it a business critical VoIP service, or a user streaming video content. QoS polices are essential to ensure business-critical applications get sufficient bandwidth. WhatsUp Gold verifies Quality of Service over through Type of Service (QoS over ToS); DSCP for LAN/WAN, CBQoS policies and Cisco NBAR classification mechanisms.
Historical Trends Identification
By studying traffic patterns and usage over a period of time, and by analyzing the data, WhatsUp Gold can identify trends in bandwidth usage and potential bottlenecks. The historical data also aids administrators in capacity planning; efficient purchase of hardware/bandwidth and also verifies bandwidth-based billing including “burstable” bandwidth services using 95th percentile reports.
Identify Abnormal Bandwidth Usage
By monitoring real-time bandwidth usage along with historical bandwidth trends, WhatsUp Gold can proactively identify security issues like DDos attacks; unauthorized downloading and other suspicious, potentially malicious, network behavior. It can aid in security forensics and analysis by automatically identifying high traffic flows to un-monitored ports; expose unauthorized applications like file sharing and video streaming; monitor traffic volumes between pairs of source and destinations; and detect failed connections.
Monitor Bandwidth with WhatsUp Gold
WhatsUp Gold uses NetFlow, jFlow, and sFlow to monitor network bandwidth and application traffic. It automatically discovers NetFlow enabled routers and switches, and configures them to collect and send NetFlow data back to it. WhatsUp Gold then analyzes the data, providing details on traffic identification, historical trends and QoS through ToS verification. Comprehensive reports showing Top Protocols, Top Senders, Top Application etc, are provided.
Download Your Free Trial
Complete the form to download your free trial of WhatsUp Gold.
Download link will be emailed to you.
Click here for latest system requirements.