What Is Network Topology?
Network topology refers to the physical or logical arrangement of the nodes, devices, and links in a network. It determines the way data is transmitted between different components and affects network performance, scalability and fault tolerance.
Network Topology Types
Admins have several options when choosing which network topology to use. The choice will depend in part on the size and scale of their organizations, their business goals, and their budget.
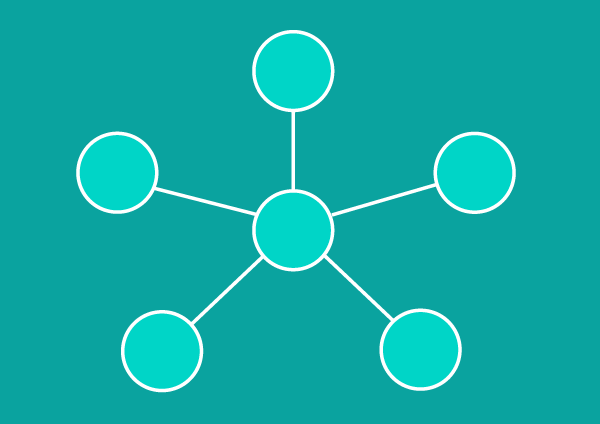
Star Topology
Star topology is the most common type of setup you’ll find. The network is arranged so that nodes are connected to a central hub, which acts as a server. The hub manages data flow across the network. In other words, any piece of data sent through the network travels through the central hub before ending at its destination.
PROS:
- Convenient management from one central location
- If one node fails, the network still functions
- Devices can be added or remove without taking the network down
- Easier to identify and isolate performance issues
CONS:
- If the central hub fails, your entire network goes down
- Performance and bandwidth is limited by the central node
- Can be expensive to operate
Bus Topology
Sometimes called backbone topology or line topology, a bus topology orients devices along a single cable running from one end of the network to the other end. Data will flow along the cable as it travels to its destination.
PROS:
- Cost-effective for smaller networks
- Simple layout; all devices connected via one cable
- More nodes can be added by lengthening the line
CONS:
- The network is vulnerable to cable failures
- Each node added slows transmissions speeds
- Data can only be sent in one direction at a time
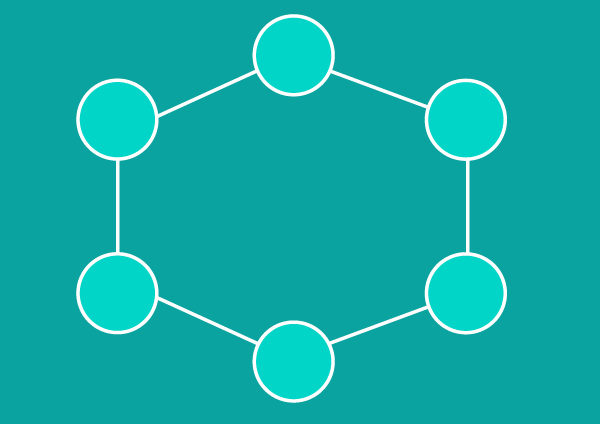
Ring Topology
In a ring topology, nodes are configured in a circular pattern. Data travels through each device as it makes its way around the ring. In a large network, repeaters may be necessary to avoid packet loss during transmission.
PROS:
- Cost-effective
- Inexpensive to install
- Easy to identify issues or performance issues
CONS:
- If one node goes down, it can take multiple nodes down with it
- All devices share bandwidth which can limit throughput
- Adding or removing nodes means downtime for the entire network
Ring topologies can be set up as single ring (half-duplex) or dual ring (full-duplex) to allow traffic to flow in both directions simultaneously.
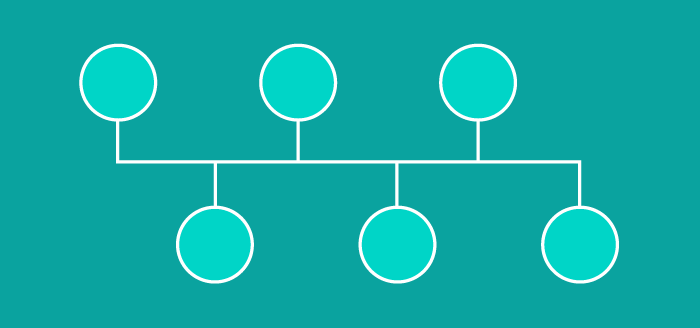
Tree Topology
In a tree topology, a central node connects secondary hubs. These hubs have a parent-child relationship with devices. The central hub is like the tree’s trunk. Where branches connect are the secondary hubs or controlling nodes, and then connected devices are attached on the limbs.
PROS:
- Extremely flexible and scalable
- Often used word WANs to support spread-out devices
- Branches can be assessed individually for performance issues
CONS:
- If a central hub fails, nodes will become disconnected (although branches can continue to function independently)
- The structure can be difficult to manage effectively
- Uses much more cabling than other methods
Mesh Topology
In a mesh topology, nodes are interconnected. Full-mesh modes connect every device directly to every other device on the network. In a partial mesh topology, most devices connect to others. This offers multiple pathways for data delivery. Data is delivered via the shortest distance available for transmission.
PROS:
- Reliable and stable
- No single node failure can take the network offline
CONS:
- Complex degree of interconnectivity between nodes
- Labor-intensive to install
- Uses much more cabling to connect every device.
Hybrid Topology
A hybrid topology is what you’d expect from the name. It used multiple topology structures. This is more common in large enterprises. For example, each department may have one type of topology, such as a star or line topology, but the department hub then connects to a central hub.
PROS:
- Flexibility
- Can be customized to customer needs
CONS:
- Complexity increases
- Expertise in multiple topologies is needed
- May be more difficult to determine performance issues
How Network Topology Affects Performance
Network topology significantly impacts performance by affecting data speed, latency, throughput, fault tolerance, and scalability. For instance, star topologies offer easy scalability and simplified troubleshooting, but rely heavily on a central hub, creating a single point of failure. Mesh topologies provide high reliability and optimal data flow through multiple paths but are complex and expensive to implement. Selecting the right topology helps to maintain efficient data movement, supports growth, and minimizes downtime, key factors in maintaining a high-performing network.
Best Practices for Choosing a Network Topology
Choosing the right network topology is critical for maintaining performance, scalability, and reliability in a network. Here are best practices to guide your decision:
Start by Understanding Your Network’s Purpose
Before choosing any network topology, get clear on what the network needs to do. Is it for a small office, a large enterprise, or a specialized use like a data center or remote location? Consider how many devices will be connected, how much traffic you expect, and how important things like speed and uptime are to your setup. Budget is another key factor, some topologies are cheaper to implement but harder to maintain or scale, while others offer greater reliability at a higher cost. Also, think ahead: will this network need to grow in the future? If so, flexibility and scalability should be part of your decision-making process.
Match the Topology to Your Real-World Needs
Once you know your requirements, you can start matching them to the strengths of different topologies. A simple bus might work for a small or temporary network, but it's not ideal for long-term use. A star setup is easy to manage and troubleshoot, making it great for small to mid-sized environments, just be mindful of the central hub being a single point of failure. Ring topologies offer predictable performance and are often used in campus networks, while mesh configurations provide high reliability and redundancy for critical systems, albeit at higher cost and complexity. Tree topologies are scalable and fit well in structured enterprise environments. Often, the most practical approach is a hybrid topology, blending elements to get the best balance of performance, cost, and fault tolerance.
Design with Longevity, Management, and Security in Mind
Think beyond just getting the network running, plan for how you’ll manage, secure, and grow it. Choose a design that allows you to easily add new devices or segments without disrupting the whole system. Build in redundancy where possible to avoid single points of failure. Make sure you can monitor network performance and health, ideally using tools that give you real-time visibility. Security should also be a key design element from the start, using network segmentation, VLANs, and firewalls to protect sensitive areas. Before launching your network, use simulation tools to test your design under different scenarios and make sure it performs as expected.
How to Map Your Network Topology
Effective network topology management requires detailed visual mapping across multiple layers of the OSI model. Regardless of the topology you deploy, whether star, mesh, or hybrid, maintaining an accurate and up-to-date network diagram is essential. These maps should include all devices, Layer 2 interconnections such as switches and MAC addresses, as well as Layer 3 elements like routers, IP addressing, and subnet boundaries. Identifying potential points of failure or congestion in advance greatly improves your ability to troubleshoot quickly and minimize downtime. In many industries, maintaining this level of network visibility is also critical for compliance with standards like PCI-DSS, especially in environments handling sensitive data such as credit card transactions.
As networks become increasingly complex and dynamic, network topology maps serve as a backbone for operational resilience and business continuity. They offer a comprehensive view that spans both Layer 2 and Layer 3, helping IT teams understand how traffic flows, how devices communicate, and where risks may lie. Fortunately, modern discovery and mapping tools, such as WhatsUp Gold, can automate this process. These tools detect and map every device connected to the network, from access points to core routers, often within minutes. As changes occur, these maps update in real-time, ensuring you always have the most current and accurate representation of your network’s topology and structure.