A network map is a visual representation of the devices and connections that make up an IT network. For IT professionals, network maps are essential tools for monitoring performance, troubleshooting issues, enhancing security and planning infrastructure upgrades.
There are multiple types of network maps, each serving a specific purpose, ranging from physical layout diagrams to cloud-based and security-oriented architectures. This article explores various network map examples, explaining their unique roles and how they support effective IT operations.
What is a Network Map?
A network map illustrates the layout and relationships within an IT environment, showing how routers, switches, servers, firewalls, endpoints and other devices are interconnected. These maps help IT professionals:
Identify the source of issues quickly
Monitor network performance and security
Plan for expansions and upgrades
Network maps generally fall into two categories:
Physical network maps – Show the actual physical layout and hardware connections.
Logical network maps – Focus on data flows, network segmentation and virtual relationships between devices.
Types of Network Maps with Examples
Below are key types of network maps used by IT and security teams, along with relevant examples and use cases.
Physical Network Map
Physical network maps display the actual locations and physical connections of network hardware, including routers, switches, servers, desktops and other devices. These diagrams are typically used to visualize how devices are physically arranged and connected to the network.
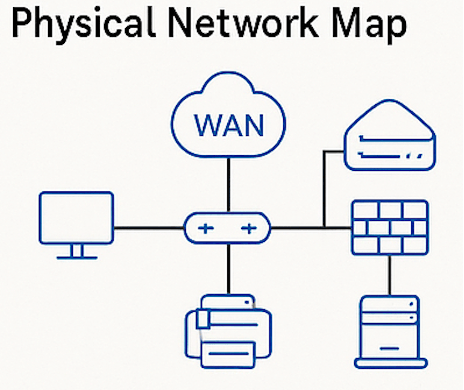
Use Case:
Tracking device locations
Infrastructure audits
Cabling management
Troubleshooting physical connectivity problems
Logical Network Map
Unlike physical maps, logical network maps don’t reflect device locations but rather the relationships and interactions between components. They also focus on the logical structure of the network, including data flows, IP subnets, VLANs and routing paths.
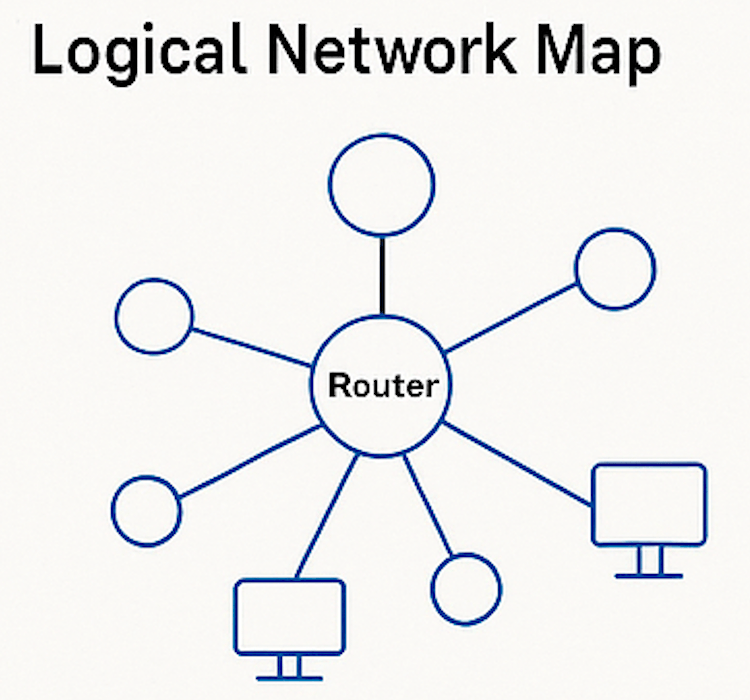
Use Case:
Understanding data flow
Designing network segmentation
Managing VLANs and routing
Planning access control policies
Cloud Network Map
Cloud network maps show how resources are organized and connected within cloud environments like AWS, Microsoft Azure or Google Cloud. These maps are essential for teams managing virtualized infrastructure across multiple regions or services.
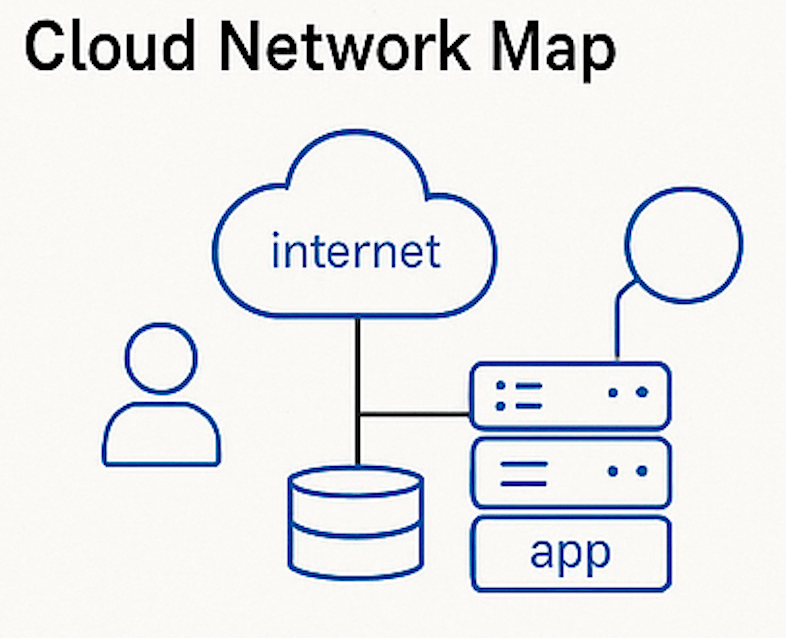
Use Case:
Visualizing cloud architecture
Managing cloud services and integrations
Identifying security gaps
Monitoring resource usage and cost efficiency
Security-Focused Network Map
Security-focused network maps are designed to help security teams identify and mitigate risks. These maps often include components like firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), demilitarized zones (DMZs) and endpoint protection layers.
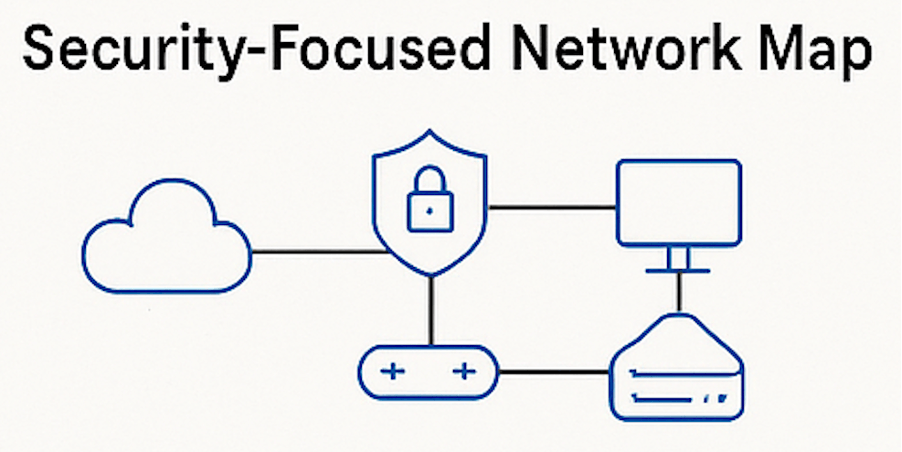
Use Case:
Risk assessment and mitigation
Identifying vulnerable zones
Planning incident response
Maintaining compliance with security standards
Hybrid Network Map
A hybrid network map combines on-premises infrastructure with cloud-based components. It provides visibility into how traditional and cloud systems interact, which is critical in modern environments where workloads are distributed.
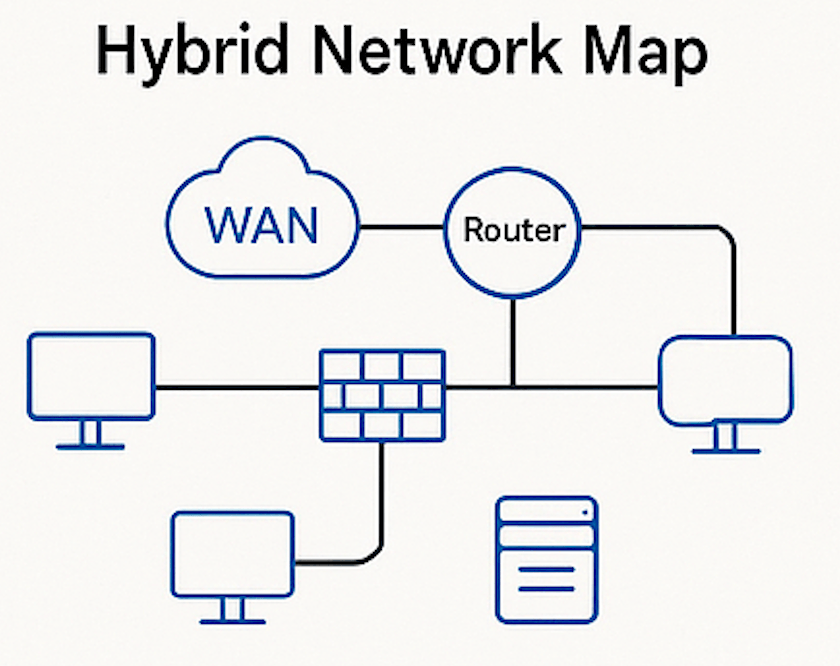
Use Case:
Managing hybrid IT environments
Maintaining consistent connectivity
Coordinating on-premises and cloud identity management
Planning scalable infrastructure
How to Choose a Tool for Creating Network Maps
Choosing the right network mapping tool enables you to create accurate, up-to-date and scalable diagrams. Look for features such as:
Automated discovery of devices and topologies
Real-time updates to reflect current network status
Customizable elements such as icons, labels and layers
Security features, including role-based access
Cloud compatibility for hybrid and virtual environments
Why Use WhatsUp Gold?
Progress WhatsUp Gold network monitoring offers powerful, intuitive tools for creating and managing network maps:
Automatically discovers all connected devices
Updates maps in real time as the network changes
Supports both physical and logical visualizations
Offers cloud and hybrid network mapping capabilities
How to Create Effective Network Maps
Creating effective network maps involves more than just plotting icons. Follow these best practices to ensure your diagrams are useful and reliable:
Keep maps updated to reflect real-time changes in infrastructure
Use clear labels and standardized icons to improve readability
Avoid clutter by organizing maps into layers or sections
Restrict access to sensitive maps to protect network information
Final Thoughts
Whether you’re managing an enterprise data center, a cloud-based architecture or a hybrid environment, network maps provide the visibility needed to maintain performance, security and scalability.
By understanding different network map examples—including physical, logical, cloud, security and hybrid diagrams—you can choose the right tools and strategies for your organization’s unique needs.
Ready to gain deeper insight into your network?
